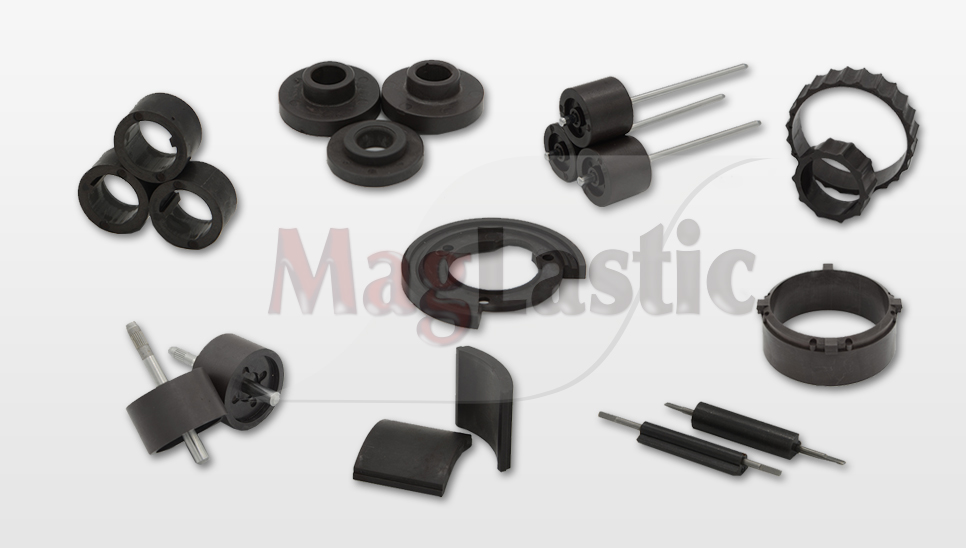
In order to maintain the flexibility of the bonded magnets made of rubber magnets, magnetic powders with a particle size of 1-1.5 μm are generally used, and the amount of binder added is also large, therefore, the magnetic properties of bonded magnets made by this process are low.
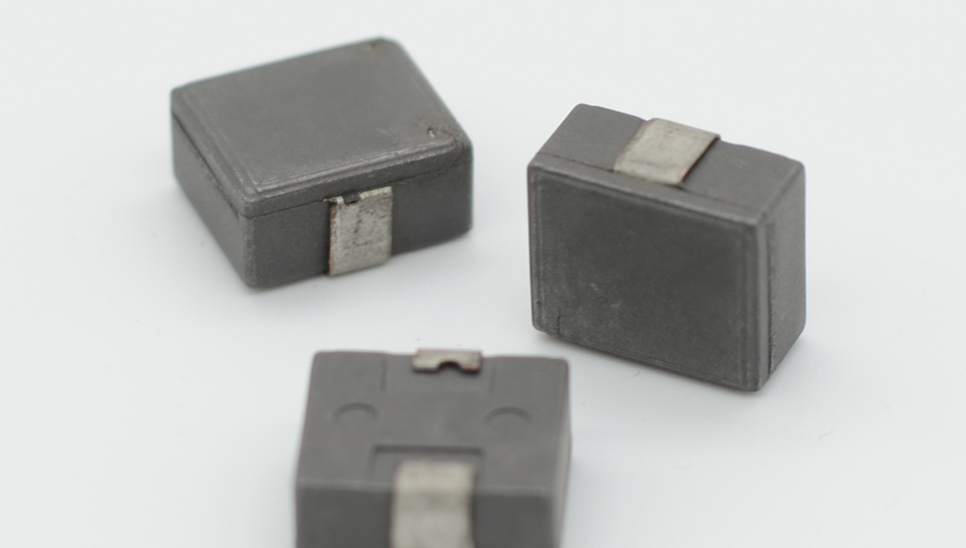
For the injection molding process, in order to ensure the fluidity of the magnetic powders and the strength of the magnets, it is also necessary to add more binders, and the overall performance of bonded magnets is higher than that of rubber magnets, fast-quenched NdFeB permanent magnet powders, HDDR powders, samarium iron nitrogen powders and other rare earth powders (samarium cobalt, aluminum nickel cobalt, etc.) can also be used as raw materials to improve product performance. The maxium magnetic energy product (BH) of injection molded magnetic materials produced by Chase Technology can reach more than 120kJ/m3.
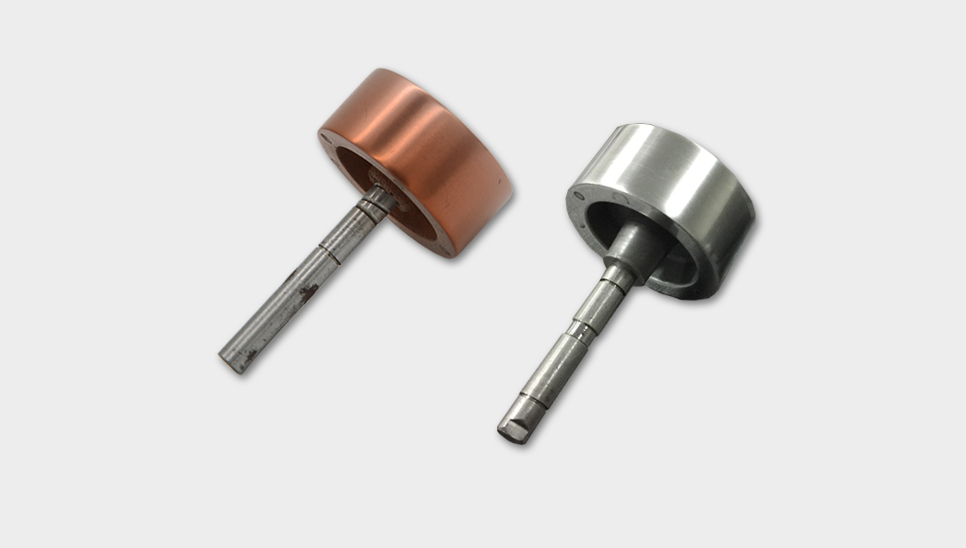
The injection molding process can produce anisotropic magnets, that is, adding a certain constant magnetic field or pulsed magnetic field when the pellets are injected into the mold to improve the magnetic properties of the injection molded magnets. This performance has once again enriched the application of injection molded permanent magnets in the industrial field, which can be used in instruments and meters, such as speedometers, fuel meters and current and voltmeters of automobiles, ships as well as airplanes. Besides, it can also be used in micro motors, printer plates, large billboards as well as children's toys, etc.
Due to the limitations of process and production equipment, the rolling and extrusion molding processes are mostly used for ferrite magnetic powders, and the magnetic properties of the products are relatively low. There are many types of powders available for injection molding, especially after the emergence of fast-quenched NdFeB permanent magnet powders, injection molded NdFeB products have also developed rapidly, playing an irreplaceable role in some areas with higher performance requirements.

Other Functional Composite Materials In addition to bonded magnetic compounds, we can also cooperate with customers to develop customized functional composite materials, such as high-density compounds and metal bonded plastic. We are committed to providing customers with new user experience and different design inspiration.
 CN
CN











 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  1F, Building 3, NO.77 Gaoxin 13 road, Xiaoshan district, Hangzhou
1F, Building 3, NO.77 Gaoxin 13 road, Xiaoshan district, Hangzhou